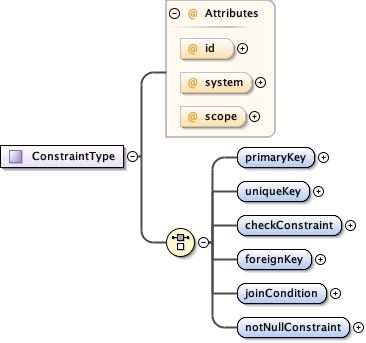
<xs:complexType name="ConstraintType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Relational integrity constraint descriptors summary: Describes the relational integrity constraints of a relational database. description: The ConstraintType type describes the relational integrity constraints of a relational database. This includes primary keys, foreign keys, unique keys, etc. When an eml-constraint module is created, it should be linked into a dataset using the "triple" element, and all of the entities that are referenced in the constraints should be accessible within that same package.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:choice>
<xs:element name="primaryKey">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Primary Key summary: The primary key in the entity description: The primaryKey element declares the primary key in the entity to which the defined constraint pertains.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
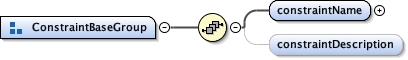
<xs:group ref="ConstraintBaseGroup"/>
<xs:element name="key">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Key summary: The set of attributes to which this constraint applies. description: The key element defines the set of attributes to which this constraint applies. For a primary key or a unique key, the set of attributes must be identifying. For a foreign key, the set of attributes must match an identifying key in the referenced entity. For a 'not null' constraint, the key indicates the attribute which should not be null.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="attributeReference" type="res:NonEmptyStringType" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Attribute Reference summary: The identifier of an attribute found in the identified entity description: The attributeReference element is the identifier of an attribute that can be found in the identified entity. This id will be unique within an entity and specifies that the attribute participates in the key that is being defined.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="uniqueKey">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Unique Key summary: A unique key in the entity description: The uniqueKey element represents a unique key within the referenced entity. This is different from a primary key in that it does not form any implicit foreign key relationships to other entities, however it is required to be unique within the entity.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="ConstraintBaseGroup"/>
<xs:element name="key">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Key summary: The set of attributes to which this constraint applies. description: The key element defines the set of attributes to which this constraint applies. For a primary key or a unique key, the set of attributes must be identifying. For a foreign key, the set of attributes must match an identifying key in the referenced entity. For a 'not null' constraint, the key indicates the attribute which should not be null.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="attributeReference" type="res:NonEmptyStringType" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Attribute Reference summary: The identifier of an attribute found in the identified entity description: The attributeReference element is the identifier of an attribute that can be found in the identified entity. This id will be unique within an entity and specifies that the attribute participates in the key that is being defined.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="checkConstraint">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Check Constraint summary: A constraint which checks a conditional clause within an entity. description: The checkConstraint element defines a constraint which checks a conditional clause within an entity.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="ConstraintBaseGroup"/>
<xs:element name="checkCondition" type="res:NonEmptyStringType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Check Condition summary: An SQL statement or other language implementation of the condition for a check constraint. description: The checkCondition element defines an SQL statement or other language implementation of the condition for a check constraint. Generally this provides a means for constraining the values within and among entities.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="language" type="xs:string" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Language summary: The language that the is used to express or implement the check constraint. description: The language element declares the language that is used to implement the check constraint. This is typically the name and version of a programming language such as Java, C, Perl, Basic, or other. Sometime it is the name and version of a scriptable analysis system such as SAS, Matlab, R, or SPlus.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
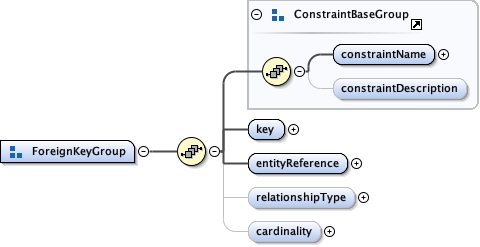
<xs:element name="foreignKey">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Foreign Key summary: A foreign key relationship among entities description: The foreignKey element defines a foreign key relationship among entities which relates this entity to another's primary key.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:group ref="ForeignKeyGroup"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="joinCondition">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Join Condition summary: A non primary/foreign key join description: The joinCondition element describes any join of two tables that is not done with a primary/foreign key relationship.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="ForeignKeyGroup"/>
<xs:element name="referencedKey">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Key summary: The set of attributes to which a foreign key constraint refers. description: The referencedKey element defines set of attributes to which a foreign key constraint refers. If the key refers to the primary key in the referenced entity, then the "referencedKey" is optional. For a foreign key, the set of attributes must match an identifying key in the referenced entity.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="attributeReference" type="res:NonEmptyStringType" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Attribute Reference summary: The identifier of an attribute found in the identified entity description: The attributeReference element is the identifier of an attribute that can be found in the identified entity. This id will be unique within an entity and specifies that the attribute participates in the key that is being defined.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="notNullConstraint">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Not Null Constraint summary: A constraint that indicates that no null values should be present for an attribute. description: The notNullConstraint element defines a constraint that indicates that no null values should be present for an attribute in this entity.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="ConstraintBaseGroup"/>
<xs:element name="key">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Key summary: The set of attributes to which this constraint applies. description: The key element defines the set of attributes to which this constraint applies. For a primary key or a unique key, the set of attributes must be identifying. For a foreign key, the set of attributes must match an identifying key in the referenced entity. For a 'not null' constraint, the key indicates the attribute which should not be null.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="attributeReference" type="res:NonEmptyStringType" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>tooltip: Attribute Reference summary: The identifier of an attribute found in the identified entity description: The attributeReference element is the identifier of an attribute that can be found in the identified entity. This id will be unique within an entity and specifies that the attribute participates in the key that is being defined.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="res:IDType" use="optional"/>
<xs:attribute name="system" type="res:SystemType" use="optional"/>
<xs:attribute name="scope" type="res:ScopeType" use="optional" default="document"/>
</xs:complexType> |